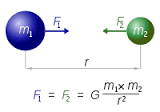ELEMENTARY ASTRONOMY
This word astronomy is defined from Greek word Astronomy which means law or others.
Hence literally meaning of astronomy is law of the stars.
ASTRONOMY
Is the branch of science that deals with the study of original evolution composition, distance and motion of all bodies (objects) and scattered matter in the universe.
UNIVERSE
Is the totality of space and time together with matter and energy.
IMPORTANCE OF ASTRONOMY TO MAN KIND
- It was earliest method of measuring time.
- It was used in develop calendars that made at possible predict the season.
- It was used in both land on sea navigation based on the knowledge of the position of the sun during the day and the stars at night.
- Astronomy presents a new frontier for exploration.
SOLAR SYSTEM
Is the system consisting of the sun, planets and their satellites, the minor planets, comets, meteoroids and other objects revolving around the sun

STAR AND PLANETS
STAR
Is the large celestial body made of hot gaseous known plasma.
PLASMA
Refers to joined gas in a certain proportion of electron and free than bound to an atom or molecules.
Stars radiate energy derived from thermonuclear on in the interior region.
The distance from the earth to the sun is about 199. 6million km this distance is called Astronomical unit”
GALAXY
Is the grant collection of stars gases and dusts.
MILKY WAY GALAXY
Is the galaxy that contains our solar system it is estimated to contain 100 – 400 billion stars.
ZODIAC LIGHT
Is a faint, diffuse and roughly triangular white glow visible in the night sky that appears to extend from vicinity of the sun along the Zodiac (ecliptic)
Zodiac light are caused by sunlight scattered by space dust in the zodiac cloud
It appears in East or west
PLANET
Is the major charge object which is in orbit around a star.
There are eight planets in our solar system, which are mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANET
- It is celestial body that orbits a star.
- It is a massive enough so that its own gravity causes it to assume hemispherical shape.
NOTE:-
Pluto no longer considered as planet because has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit. Pluto resides in an area of space populated by numerous others object. Pluto now designated a dwarf planet”
DIFFERENTIATES BETWEEN STARS AND PLANETS
- Emit their own light where planet Do not emit their own light.
- Twinkle at night where planet Do not twinkle at night.
- Appears to be moving from cast to west where planet Planet move around the sun from west to last
- Their temperatures are us usually very high.where planet Their temperature depends on the disk once from the sun.
- countless in number where planet Their eight in the solar system
- Very bigger in size but they appear small because they are very far way.where planet Very small in size compared to stars.
ASTEROIDS
Are small solar system bodies’ in orbit around the sun especially in the inner solar system.
Are same times known as minor planets.
COMETS
Is a solid body orbiting the sun typically composed of rock.
METEOROID
Is a chunk of rock or dust in space
METEOR
Is streak of light in the sky produced by burning of a meteoroid in the earth’s atmosphere
OR
Is a bright trail or streak that appears in the sky when a meteoroid is heated to incandescence by friction with the earth’s atmosphere
METEORITE
Is a meteoroid that has hit Earth’s surface
GRAVITATIONAL FORCE
Is an attractive force existing between any two objects that have mass
NEWTON’S LAW OF UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION
The Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation states that;
“Any two objects attracts each other by the force which is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them”
Where the Gravitational constant, G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/Kg2
CONSTELLATIONS
Is a group of stars that form a definite shape or pattern when viewed from the earth.
Examples of constellations are
OTHER CONSTELLATIONS
USES OF CONSTELLATIONS
- RELIGIOUS
In early days, people thought that the gods lived in the heavens and that the gods created the constellations. Many cultures believed that the position of the stars were their god’s way of telling the stories.
- AGRICULTURAL
Before there were proper calendars, people had no way of determining when to sow or harvest except by the stars.
- NAVIGATION
One can figure out his or her latitude (North or South) just by looking at how high Polaris appears in the sky.
THE MOON OF THE EARTH
The moon of the earth is the heaven that revolves around the earth.
Properties of the moon of the earth are;
- Is the sixth largest in the solar system
- It has diameter of 3476 Km and mass of 7.35 x 1022 Kg
Note:
- PERIGEE
Is where the moon become nearest to the earth, about 356000 km
- APOGEE
Is where the moon become furthest to the earth, about 406000 km
- The temperatures on the moon’s surface are on average 107° during the day and -53° during the night
- Made up of iron core surrounded by a rocky mantle and crust
- Does not have a magnetic field
- Surface gravity on the moon is 1/6 that on the earth.
- Revolves the earth in an anticlockwise direction in an elliptical orbit.
- It takes 27.3 earth days to complete one orbit.
- The average distance from the moon to the earth is 384000 km
OCEAN TIDES
Tides are periodic rises and falls of the large bodies of water. Tides are caused by the gravitation interaction between the earth and the moon.
The ocean is constantly moving from high tides to the low tides and then back to the high tides. There is a time interval of about 12 hours and 25 minutes between the two high tides.
How ocean tides occurs
The gravitation attraction of the moon causes the ocean to bulge out in the direction of the moon. Another bulge occurs on the opposite side since the earth is also being pulled toward the moon. Ocean level fluctuate daily as the sun moon and the earth interact. As the moon travel around the earth, and they together travel around the sun, the combined gravitational force cause the world ocean water level to rise and fall. Since the earth rotating while this is happening, two tides occur each day.
Types of tides
- Spring tides
This is a type of tides which occurs during the full moon and the new moon. During this time the moon the earth and the sun are arranged in a line.
- Proxigean spring tides
The Proxigean spring tides are a rare unusually high tide. This occurs when the moon is both usually close to the earth (at its closest perigee called proxigee) and in the new moon phase (when the moon is between the sun and the earth). The Proxigean spring tide occurs at the most once every 1.5 years.
- Neap tides
This is an ocean tides which occurs during the quarter of the moon. During this time, the gravitation force of the moon and the sun is perpendicular to one another with respect to the earth.